How Circusol Powers a Circular Economy
The CIRCUSOL project (Circular Business Models for the Solar Power Industry) is a European initiative funded by the Horizon2020 Programme of the European Commission and supported by the Executive Agency for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (EASME). CIRCUSOL aims to establish solar power as a spearhead sector to demonstrate a path driven by Product-Service System (PSS) business models towards a circular economy in Europe.
How does CIRCUSOL advance the closed-loop business model?
CIRCUSOL focuses on circular product-service system business models (PSS), in which the supplier remains the product owner and the customer pays for the performance or functionality delivered by the product. A well-known example is Philips Pay-Per-Lux, where customers pay for the light instead of the lamp. In theory, PSS models could incentivize suppliers to extend product lifetimes and minimize use phase costs. Therefore, they are widely seen as a key solution for circular economy. But PSS models don’t automatically lead to circular economy. To live up to such high expectations, PSS models need to deliver real environmental benefits. They also need to deliver successful business and be competitive and financially healthy in order to survive and thrive. These are the three key success factors for PSS which CIRCUSOL is working on: real environmental benefits, market fit and financial health. We want to show how PSS models can really work for circular economy in the real world.
How big is the market for reusing solar PV panels, both in Europe and globally?
This is a key question CIRCUSOL will answer. Solar PV is a young product. Most deployed PV panels are still in use and there is no existing reuse market yet. But the volume of used PV panels will soon rise, opening opportunities for the reuse market. CIRCUSOL aims to pave the way for reuse by developing reuse and refurbish supply chains and by stimulating market demand with PSS models. We will also run an application and market analysis to identify the “sweet spots” for reusing solar PV. The same goes for reusing batteries from electric vehicles (for solar power storage in connection to PV), which is the other product group CIRCUSOL is looking into.
How do the five CIRCUSOL demonstration pilots work and where are they based?
The five CIRCUSOL demonstrators are set up to validate the three key success factors of circular PSS models: real environmental benefits, market fit and financial health. They are real-life commercial pilots with real customers. CIRCUSOL industrial partners (Futech, Ecopower, BKW and SOREA) will provide second-life solar panels and batteries as a service for homes, shops and solar farms in Belgium, France and Switzerland. The services will be co-created with the customers to ensure they are market-fit. The second-life PV and batteries are not subsidized by CIRCUSOL, but instead are real investments made by CIRCUSOL partners. The academic partners will evaluate (ex-ante) the environmental impacts from the very beginning to screen and steer business model design decisions. The business models will first be demonstrated at single sites, then scaled at regional level.
How will the ICT system envisaged by CIRCUSOL add value to the product-service system?
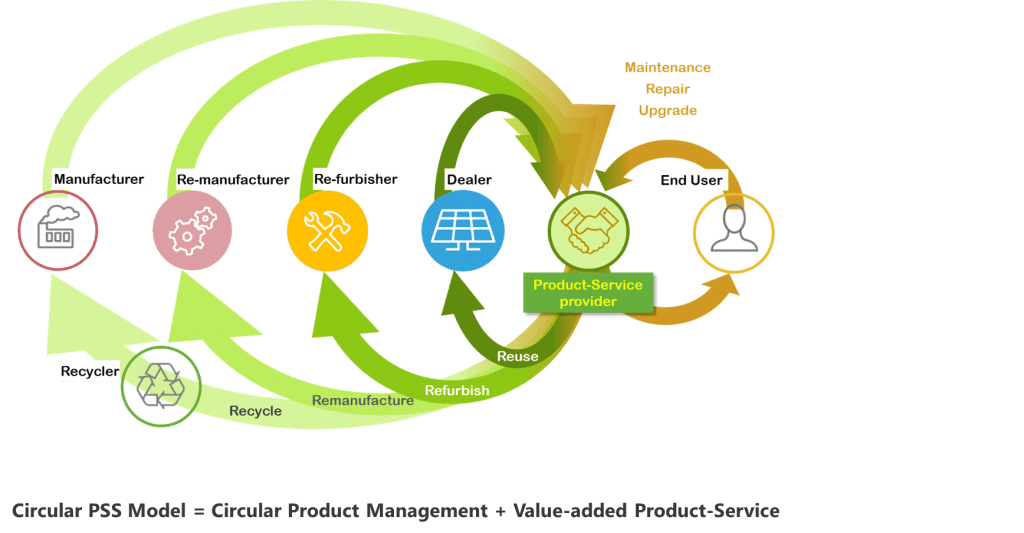
In the circular PSS business models envisioned by CIRCUSOL, the service provider will take back the products (PV and battery) at the end of their service life. The service provider then needs to decide whether the used products are suited for direct reuse, refurbishing, remanufacturing, or recycling. Data is needed to support this important decision. This can include manufacturing data (such as materials, components and assembly methods), installation data (such as location and connections), usage data (such as number of operating years and electricity production/storage performance). CIRCUSOL plans to prototype an ICT platform to collect, store and share such information in the supply chain to facilitate informed decisions. The platform can also be used by service providers to optimize use phase operations by refurbishers, remanufacturers, and recyclers to optimize their processes.
What industry or sector shift do you hope to encourage with CIRCUSOL?
We want to make solar power a spearhead sector in demonstrating a path driven by service models towards a circular economy. Solar power is a new and rapidly growing industry. Although resource management is not yet a big challenge today in this sector since the “waste” volume is still low, it will become one in the future if we continue business-as-usual. We have the opportunity now to prevent the problem from exacerbating, instead of having to change entrenched systems and repair damage retrospectively. Solar power is a flagship sector in the battle against climate change. We want to show that by taking the whole ecosystem and product life cycle into consideration from the beginning, we can avoid creating new environmental challenges while resolving the old ones, thus realizing a truly sustainable transition towards a low-carbon renewable future. We want the impact of CIRCUSOL to go beyond the solar power industry. We hope that the circular business model innovation methodologies and tools developed in CIRCUSOL will find use in other sectors to support a broader societal shift towards a circular economy.